BLOGS
Where Are the Major Fault Lines in the Philippines?
There will always be earthquakes somewhere, but that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t be concerned about them. Over a hundred earthquakes of magnitude 2 or below occur every day, according to experts. But what about earthquakes with greater intensity?
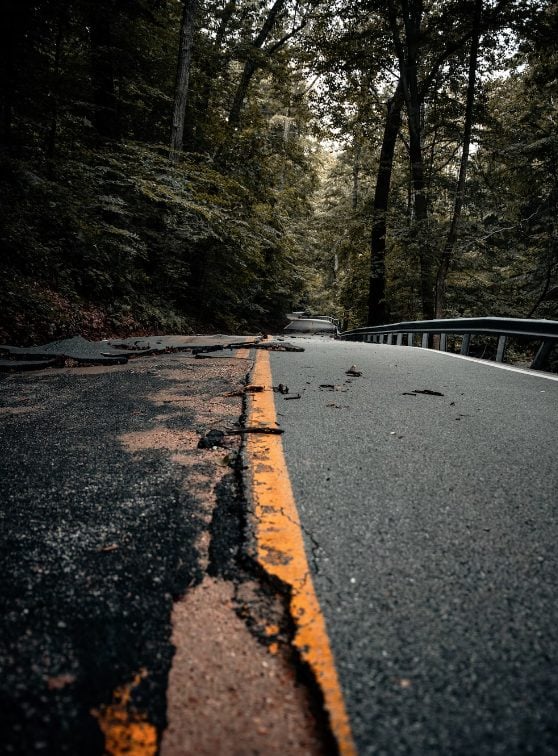

The Ring of Fire, located in the Pacific Ocean, is extremely dangerous due to its high frequency of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Regarding the Ring of Fire’s various oceanic trenches, volcanic arc systems, and plate motions.
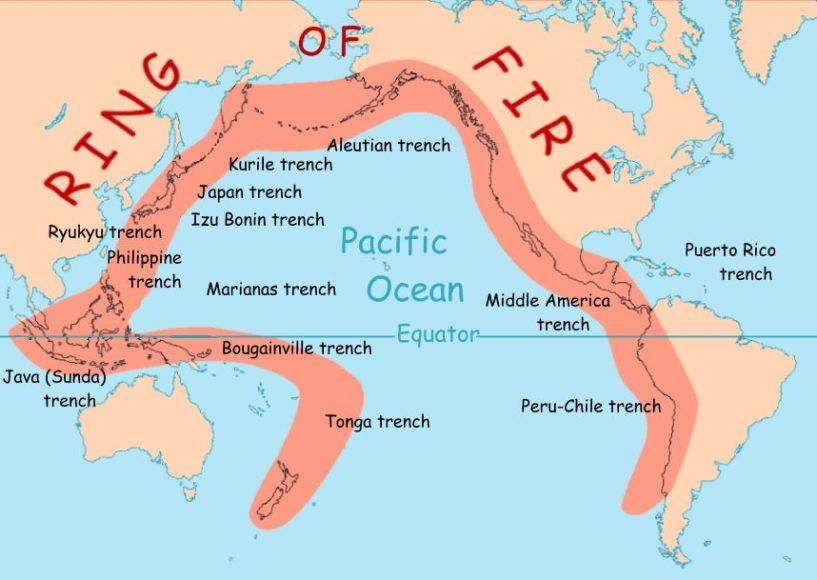
The Philippines, like any other nation, has a number of faultlines that make it particularly vulnerable to earthquakes. We’ll talk about the Philippines’ active fault lines in this section, along with how to determine whether your neighborhood is close to one.
What is a fault line?
A break in the crust that was created as the crust shifted is known as an earthquake fault. Seismologists have discovered that fault lines are where the deepest earthquakes occur. Seismic waves are produced when two fault sides pass one another, which causes the earthquake to occur.
Three tectonic plates encircle the nation: the Philippines Plate, the Eurasian Plate, and the Indo-Australian Plate. The Philippine fault zone was thus created as a result of the movement of these tectonic plates.
What are the Fault Systems?
When under stress (being forced apart or crushed) close to the Earth’s crust, rocks crack. A fracture or joint occurs when rocks split and there is no offset on either side of the break. Additionally, rocks can fracture due to thermal expansion and contraction, the consequences of fluids freezing, or when they are dragged or crushed together. A fault occurs when two rocks pass one other along a fracture surface. A “fault plane” is the term used to describe a fault surface, which is frequently almost flat.
Normal faults, reverse faults, strike-slip fault, and oblique slip faults are the four different categories of faulting. A normal fault is one in which the hanging wall or footwall of rocks above the fault plane moves downward in relation to the footwall of those rocks. When the footwall rises up relative to the hanging wall, this is known as a reversal fault. The movement is known as strike-slip motion when the rocks on each side of a nearly vertical fault shift horizontally. When movement is not exactly parallel to the fault plane, a specific type of fault called an oblique-slip fault develops. When strike-slip faults have either some normal or reverse movement or when strike-slip faults have both, oblique movement happens.
The Philippine Fault Zone
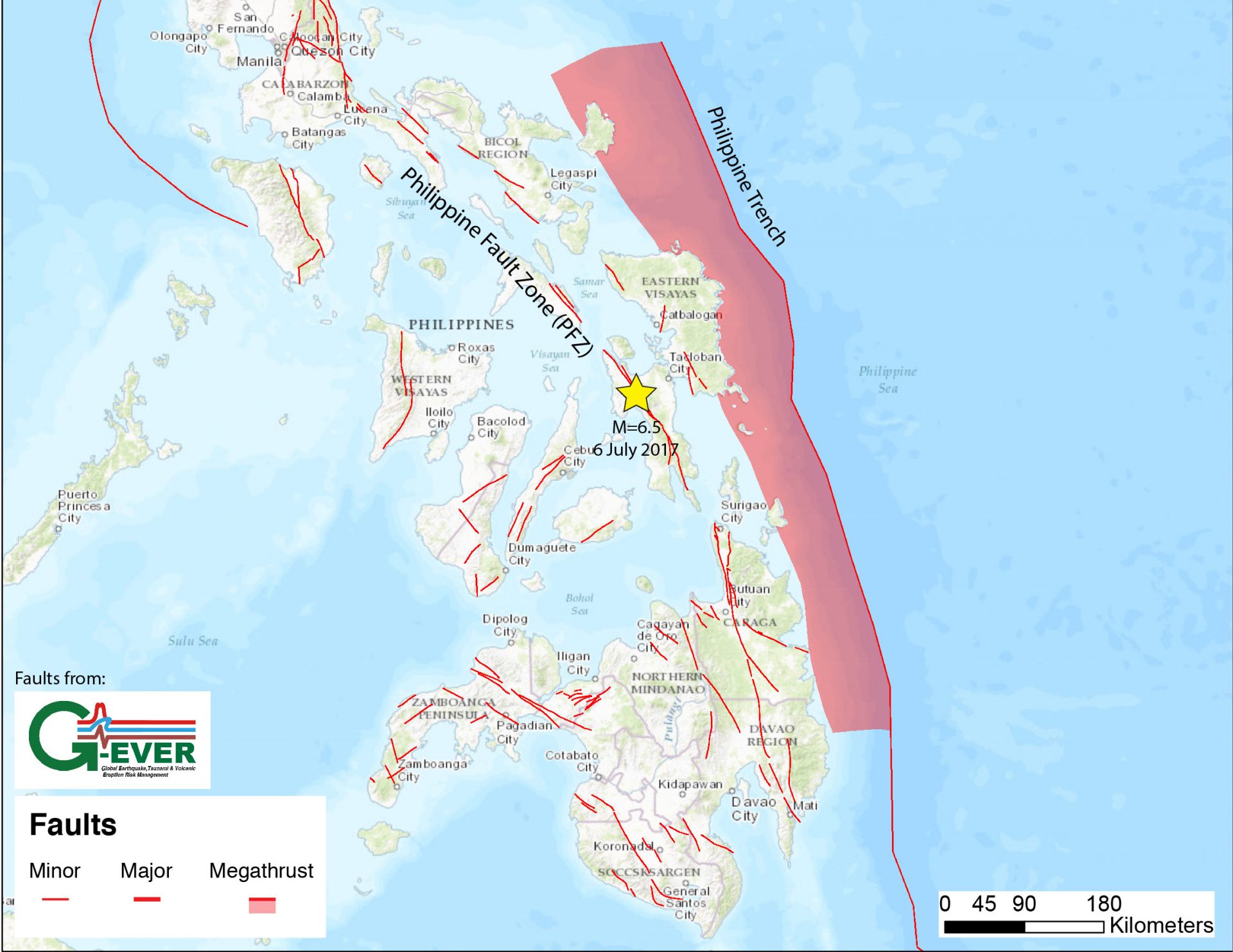
The Philippine Fault Zone (PFZ), a 1,200-kilometer (km) long geological feature that runs across the nation, may be one reason why the country frequently experience severe earthquakes. The fault zone travels across the following regions as it extends from northwest Luzon to southeast Mindanao: Ilocos Region, Nueva Ecija, Quezon Province, Masbate, Leyte, CARAGA Region, Davao Gulf, and Davao Oriental.
Notable faults in the Philippines
There are few notable faults in the Philippines that we should be aware of:
System of Marikina Valley Faults
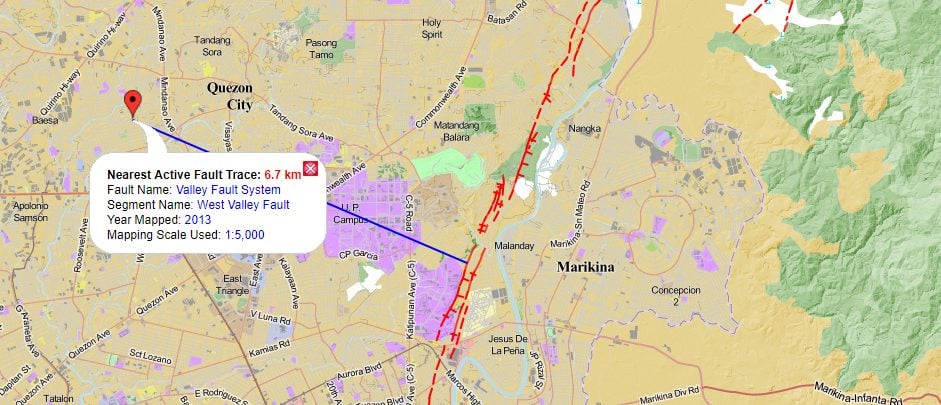
The Marikina Valley Fault is the most dangerous and nearest fault in the metro. This is due to the fact that it passes through the most populated and dynamic parts of Manila. On top of that, the Marikina Valley Fault Line is the most seismically active fault in the Philippines, according to PHIVOLCS, the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology. Additionally, it’s probable that this fault moving will result in the eruption of Taal Volcano.
Fault in Guinayangan
The Guinayangan Fault, an active fault that runs across the middle of Quezon Province and is also a member of the PFZ, is a fault that is active, according to 2020 data from the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS).
Western Philippine Fault Lines
The water level can also be a problem if you weren’t aware of it. In reality, the West Valley fault runs through the oceans of the Western Philippines rather than on land.
Philippine Fault Lines in the East
The Eastern Philippine Fault was found underground in a similar manner to how the Western Philippine Fault was. The Philippine Sea contains several active faults.
Masbate Fault
Masbate is thought to be a seismically active portion of the nation, which explains why there are so many earthquakes there. The Guinayangan Fault and the Masbate Fault are both parts of the PFZ. The Uson Fault and the Southern Masbate Fault are two additional potentially active faults in Masbate.
The shifting of the PFZ was what prompted the province to experience the magnitude 6.6 earthquake in August 2022. Aklan, Albay, Biliran, Capiz, Leyte, and Negros Occidental are nearby provinces that saw a negative influence.
Philippine Central Fault Zone
The archipelago’s fault creep, gradual slide events, and large earthquakes are all caused by the Central Philippine Fault Zone. This fault crosses multiple provinces and cities in various cities from the northern part of the archipelago down to the northern section of Davao because it is similar to the Marikina Valley Fault.
The Central Philippine Fault Lines are located in the following locations: Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Aurora, Davao del Norte, Eastern Leyte, Masbate, and Quezon, Southern Leyte as well as whole of Ilocos Norte.
The PHILVOCS Fault Finder
The Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) is a national organization in the Philippines that offers data on volcano, earthquake, and tsunami activity as well as other specialized information and services, primarily for the protection of people and property.
PHIVOLCS tracks the activity of volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis and gives alerts when appropriate. It is required to lessen the impact of disasters that could be caused by these types of geotectonic processes, including volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, tsunamis, and others.
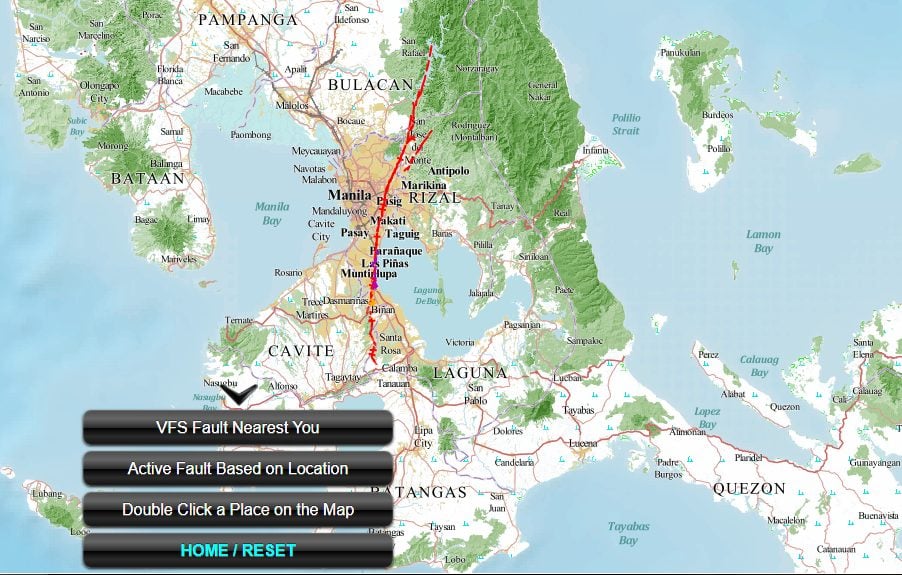
Using the PHIVOLCS Fault Finder, an official government organization secure websites, you can easily determine whether your location is near a fault. It’s time to determine whether your area is at risk of earthquakes now that you are aware of the well-known active fault lines in the Philippines. You can use PHIVOLCS Fault Finder to find out if your area is close to a fault. This online tool was developed by the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) to assist users in determining how near they are to a fault. Actually, the goal of this effort is to help people get ready for upcoming natural disasters.
Conclusion
The current situation of the Philippine fault system must be understood. In fact, by using this information in the event of a fault shifting, you might help your government agency as well as yourself.
On the other hand, the general public may also receive assistance from the PHIVOLCS Fault Finder in determining whether or not they are situated close to a fault. Additionally, if people are unfamiliar with the active fault lines in the Philippines, this may help them locate them.
In particular when purchasing a home or piece of property, consumers might gain some insight into which areas are safe from damaging and frequent earthquakes through this.
READ NEXT ARTICLE: SUMMER SOLSTICE CELEBRATION IDEAS AT HOME
READ NEXT ARTICLE: HOW TO CREATE A FINE DINING EXPERIENCE AT HOME